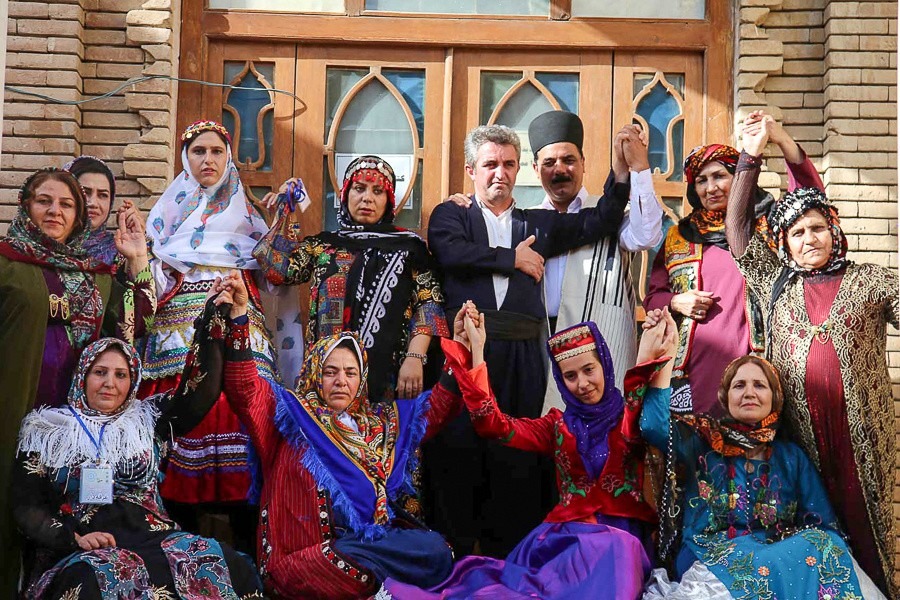
Tribes and Clans of Iran!
In Iran, many different tribes and clans come together to create a colorful and strong cultural mix. This country has lots of different groups that live together peacefully, each adding their own part to Iran’s history. Over time, these close relationships have made a lasting impact, shaping the core of the country’s identity.
When you take a closer look, you’ll see many different traditions in Iran. They’re like layers of stories, each with its own unique details. Festivals, ceremonies, and rituals are like threads that connect the past to today, carrying the history of many years while also changing with the times. Every tribe and clan keeps its own special history alive, adding different colors and designs that make Iran’s traditions lively and rich.
When the sun goes down in Iran’s rough lands, you can see the patterns of many stories in the tapestry. This shows how strong unity is, even when there are lots of differences. Among the tribes and clans, we see not just a mix of histories, but also proof that sharing common origins is important. Iran’s cultural tapestry is like a detailed artwork, celebrating the stories of its people and reminding us that many threads can come together to make one united story.
Historical Significance of Tribes and Clans
Throughout history, tribes and clans in Iran have played crucial roles in shaping the nation’s destiny. These groups often determined political alliances, engaged in trade, and even influenced historical events. Many ancient Persian dynasties were closely connected to certain tribes, and these associations continue to resonate in modern times.
Diverse Tribal Landscape
The tribal landscape of Iran is incredibly diverse, encompassing a wide range of lifestyles and cultural practices.
Nomadic Tribes
Nomadic tribes have been an integral part of Iran’s history for centuries. These nomads traverse vast expanses of the country with their livestock, following seasonal patterns in search of food and water. Their resilient way of life is a testament to adaptability and survival.
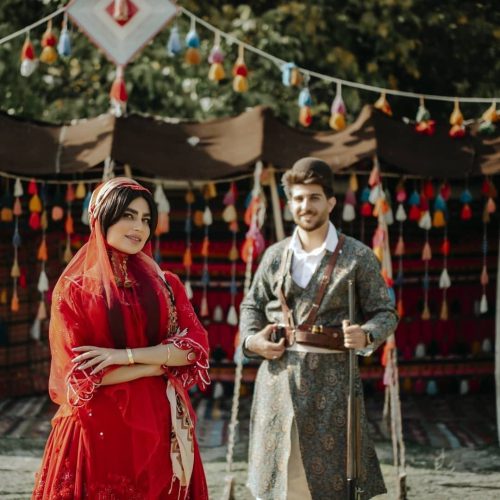

Agricultural Tribes
In contrast to nomadic tribes, there are agricultural tribes that have established settlements in fertile regions. These tribes engage in farming, horticulture, and other sedentary occupations. Their communities often boast ancient customs passed down through generations.

Social Structure and Leadership
Tribes and clans typically have hierarchical social structures with well-defined leadership roles. The head of a tribe, often referred to as the chief or chieftain, holds significant influence. This structure fosters a sense of unity and purpose among members.
Languages and Communication:
Language is a crucial part of each tribe’s identity, with many tribes having their own dialects for communicating within their community. This diverse range of languages reflects the vibrant cultural mix of Iran. Interestingly, in Iran, various tribes and clans use distinct languages to share their stories. This forms a wonderful blend of voices that resonate throughout the nation. These groups have their individual lifestyles, blending old traditions with modern practices, adding to Iran’s diversity. The community structures are like large families, fostering a sense of connection and unity as generations pass.
Cultural Traditions and Festivals
Tribes and clans celebrate a variety of festivals and traditions that reflect their way of life and belief systems.
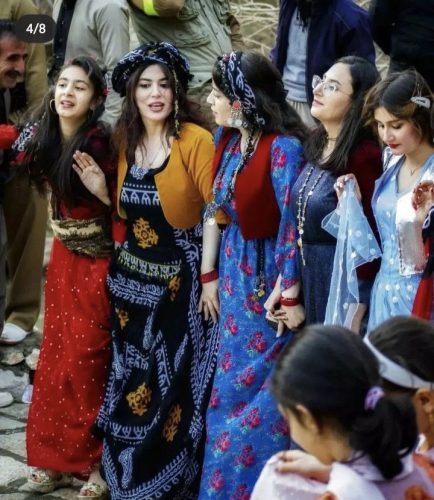

Nomadic Festivals
Nomadic festivals often revolve around nature and the changing seasons. These celebrations are marked by vibrant costumes, traditional music, and dances that narrate stories of their history.
Ceremonial Rituals
From birth to marriage and death, tribes have intricate rituals that guide life’s significant milestones. These rituals are a testament to the importance of tradition and community.
Economic Practices and Livelihoods
The economic practices of tribes vary based on their lifestyle. Nomads rely on animal husbandry, while agricultural tribes focus on cultivating the land. These practices underscore their self-sufficiency and sustainability.
The Perfect Iran Tour for First Timers
Challenges and Modern Influences
While tribes have preserved their cultural identity, modernity presents both challenges and opportunities. Access to education, healthcare, and urbanization impact traditional ways of life. Balancing tradition with progress is an ongoing endeavor.
Preservation of Tribal Identity
Efforts are underway to preserve the distinct identities of Iran’s tribes. Cultural organizations, museums, and academic research contribute to safeguarding their heritage for future generations.
Government Policies and Tribal Relations
The Iranian government acknowledges the significance of tribes and seeks to integrate them into the national framework while respecting their autonomy.
The Role of Tribes in Modern Iran
Tribes continue to play a role in Iran’s modern politics, economy, and society. Their influence extends beyond rural areas, shaping national conversations and policies
Impact on Art, Music, and Literature
The artistic expressions of tribes are woven into Iran’s cultural tapestry. Their music, dance, crafts, and folklore have inspired artists and creators for centuries.
Tribal Tourism
Tribal areas have become intriguing destinations for tourists interested in experiencing authentic Iranian culture. This form of sustainable tourism benefits both the tribes and the national economy.
Highlights of Persia Tour
The Intricacies of Inter-Tribal Relationships
Interactions between different tribes often shape regional dynamics. Cooperation, conflict, and cultural exchange have contributed to the complex web of relationships among tribes.
Let’s quickly explore Clans of Iran:
- Turkmens: The Turkmens are Turkic tribes that inhabit the Turkmen Sahra region on the eastern plains of Mazandaran and the northern areas of Khorasan provinces. Their territories are adjacent to the borders of Turkmenistan Republic.
- Kurds: Kurdish is their spoken language. As one of the oldest Iranian tribes, Kurds have a widespread presence across the nation, with a significant population in Kurdistan as well as in the provinces of Ilam, Kermanshah, and Lorestan.
- Baluches: The Baluch people inhabit the vast and less populated deserts of southeastern Iran and remote parts of western Pakistan. They are distinct for maintaining a semi-nomadic lifestyle, a rarity among Iranian tribes. Their expertise in horseback riding is noteworthy, and they are particularly famous for their camel racing events.
- Bakhtiyaries: The Bakhtiyari tribe, also referred to as Lur-e Bozorg, is a significant Lur tribe in Iran residing in the central Zagros region. The majority of Bakhtiyaries live in the remote areas of Chahar Mahal, Bakhtiyari, and Khuzestan. However, a considerable number have chosen to settle in both villages and cities.
- Qashqaees: The Qashqaees, alongside the Bakhtiyari, are one of Iran’s major tribes. Predominantly residing in Fars province, some continue the tradition of migrating between summer and winter residences annually. Of Turkic origin and Shia faith, the Qashqaees hold their rituals and traditions in high regard. Their language blends Qashqaee Turkish and Persian, but they all speak fluent Persian.
- Lurs: Descendants of the Aryan race, the Lurs have historically intermingled with the Kashi or Kasit tribes. While certain Arab and Turk groups have integrated with them over the years, the Lurs have managed to maintain their distinct identity. Comprising two percent of Iran’s population, they primarily inhabit the provinces of Luristan and Kermanshah, with a smaller presence in Hamadan.
- Persians: Accounting for over 65 percent of Iran’s population, the majority belong to the Persian ethnicity. Their lineage traces back to the Elamite and Aryan ancestral roots.
- Arabs: Constituting around 4 percent (equivalent to 2.5 million individuals) of Iran’s population, the Arab community is primarily concentrated in Khuzestan province and the Persian Gulf islands.
- Azaries: The Azari community is centered in the northwest region of Iran, encompassing West Azerbaijan and Ardebil provinces. This area serves as the principal homeland for Iranian Azaries. Comprising a significant portion, Azeri Turks make up 25 percent of the population.
Conclusion
The tribes and clans of Iran are not just historical artifacts; they are living embodiments of the nation’s diverse heritage. Their cultural practices, traditions, and languages enrich the social fabric of Iran. As the country continues to evolve, the importance of preserving and respecting these tribes remains vital.
Kabud Mosque ! A beautiful Place in IRAN